Fast API CLI란?
Fast API에서 24.05.03 Release에서 FastAPI CLI라는 신규 기능을 공개했다
어떤 점이 변화했고 추가되었는지 알아보자
Release_Note: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/release-notes/
Release Notes - FastAPI
FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production
fastapi.tiangolo.com
Docs: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/fastapi-cli/
FastAPI CLI - FastAPI
FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production
fastapi.tiangolo.com
- Fast API에 CLI를 도입하여 프로젝트관리를 보다 쉽게 할 수 있게 되었다고 한다.
사용방법
Fast API CLI는 FastAPI 0.111.0 버전 이상을 설치할 시 기본적으로 포함되어 있다.
- 기존에 Fast API를 사용하고 있던 프로젝트라면, 업그레이드하여 사용이 가능하다.
$ pip install --upgrade fastapi
- 간단한 예제를 작성하여 서버를 실행한다.
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Union[str, None] = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
- fastapi-cli 활용 앱 개발환경 실행방법
$ fastapi dev
- 터미널에 fastapi dev를 입력하여 쉽게 앱 실행이 가능하다.
- fastapi dev는 기본적으로 reload가 활성화되어 있기 때문에 코드를 수정할 경우 자동으로 다시 서버를 로드한다.
- 실서버의 경우 fastapi run을 활용하여 앱을 실행한다.
$ fastapi run: fastapi run의 경우 prod 환경에서 사용하며, reload는 활성화되어있지 않다.
또한, http://0.0.0.0:8000 주소로 서버가 가동된다.
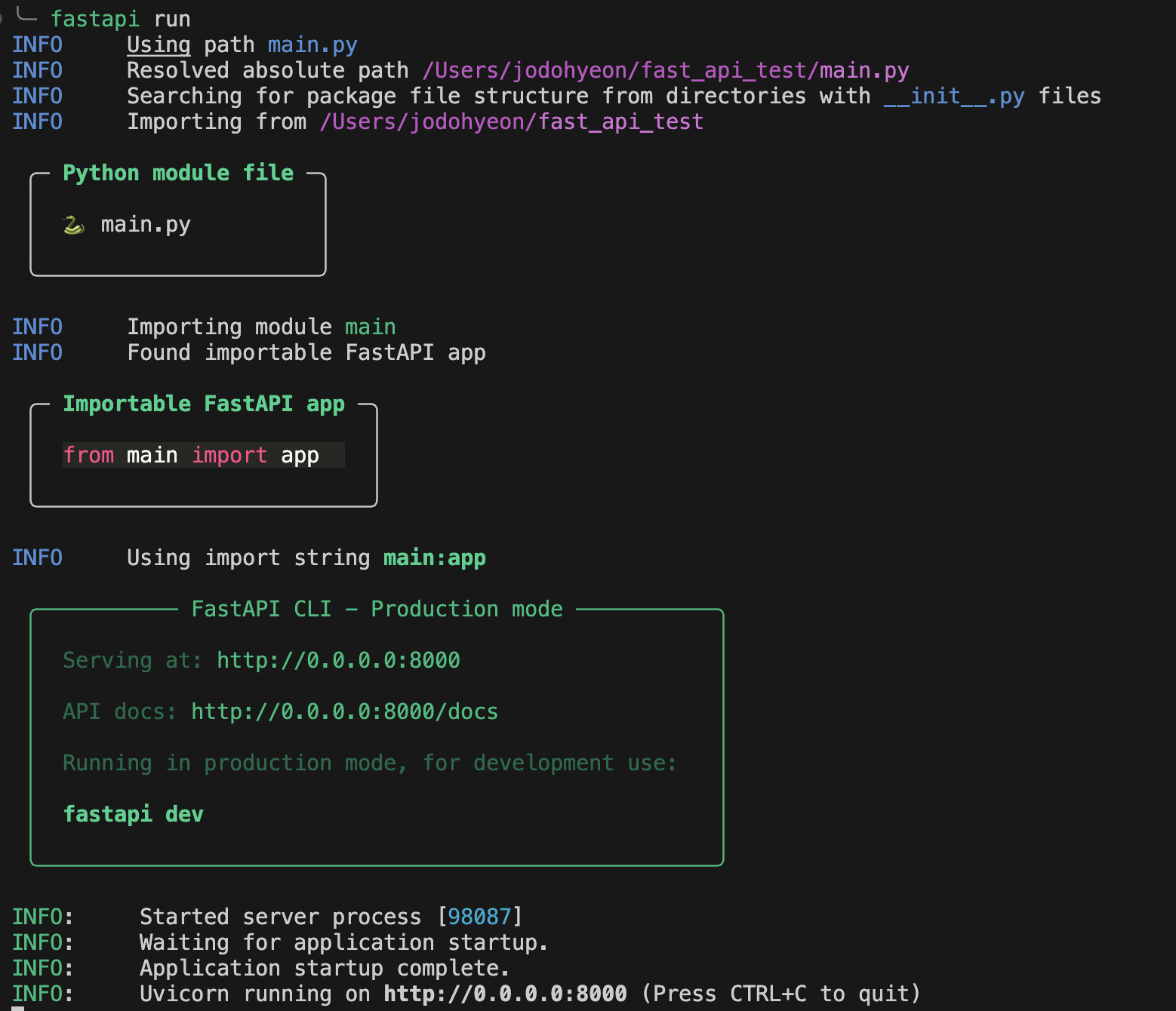
보통 main.py를 서버구동을 위한 Main파일로 사용하지만 다른 명칭의 파일을 기준으로 서버를 구동하고 싶다면 명령어에 파일명을 추가하여 구동할 수 있다.
$ fastapi dev sub_main.py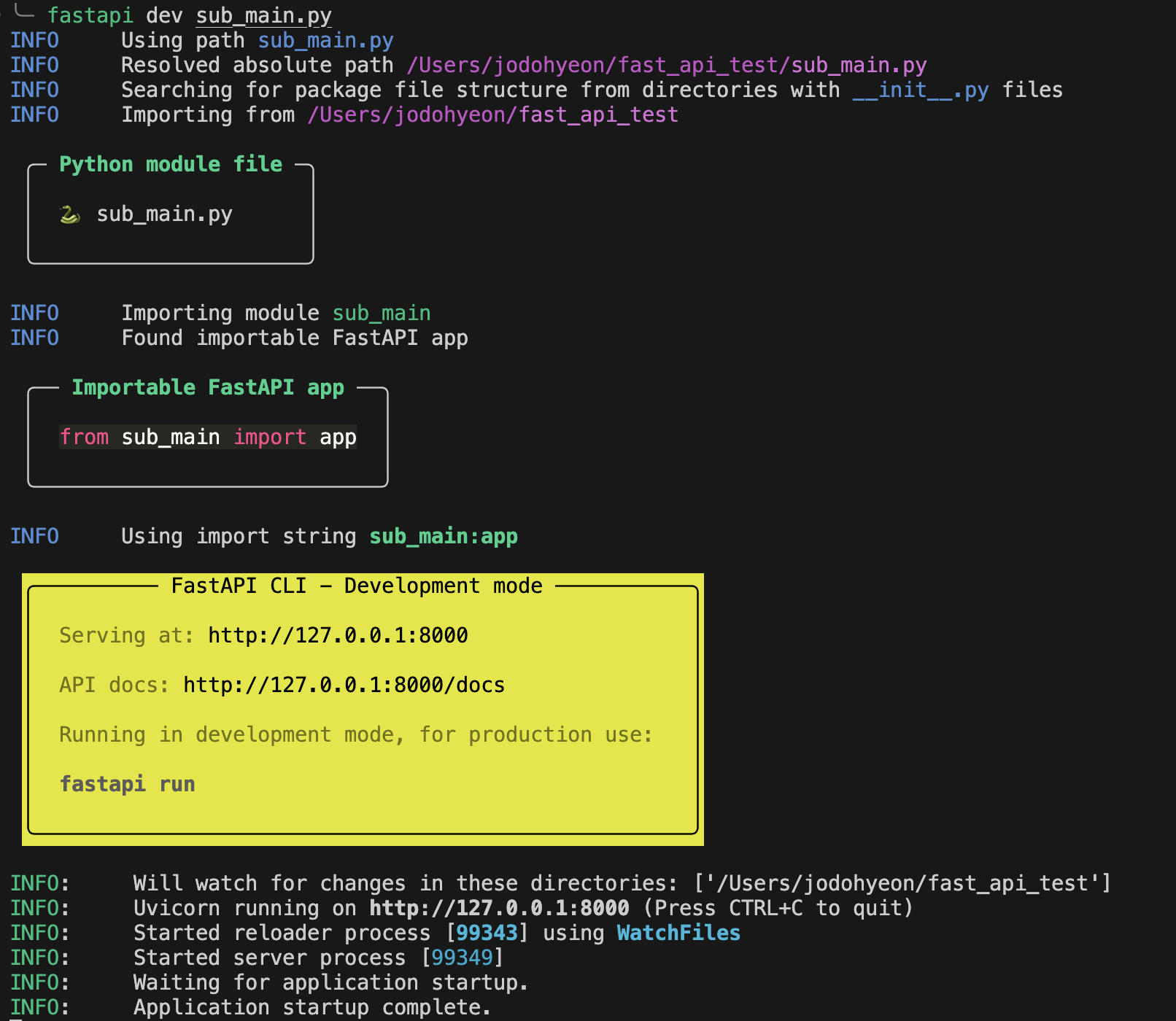
변경된 파일명으로 정상적으로 구동되는 것이 확인된다.
변화된 점 (기존방식과의 차이)
FastAPI는 기본적으로 Uvicorn이라는 ASGI 서버를 구동해줘야 한다.
이를 위해서 기본방식에서는 아래와 같은 명령어로 서버를 실행시켜 주었다.
$ unicorn main:app --reload
또는 main.py(서버구동 메인파일)에 조건문을 추가하고 파이썬파일을 직접 실행하여 dev환경에서 서버를 구동하였다.
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)하지만, 현재는 추가된 CLI를 활용하여 보다 쉬운 명령어로 FastAPI 서버를 구동할 수 있게 된 것이다.
2024.06.14(기준) 한국어 docs에는 최신화가 되어있지 않아 이전의 서버 구동방식을 가이드해주고 있다.

변경된 서버 구동방식 가이드

FastAPI CLI 소스코드 분석
@app.command()
def dev(
path: Annotated[
Union[Path, None],
typer.Argument(
help="A path to a Python file or package directory (with [blue]__init__.py[/blue] files) containing a [bold]FastAPI[/bold] app. If not provided, a default set of paths will be tried."
),
] = None,
*,
host: Annotated[
str,
typer.Option(
help="The host to serve on. For local development in localhost use [blue]127.0.0.1[/blue]. To enable public access, e.g. in a container, use all the IP addresses available with [blue]0.0.0.0[/blue]."
),
] = "127.0.0.1",
port: Annotated[
int,
typer.Option(
help="The port to serve on. You would normally have a termination proxy on top (another program) handling HTTPS on port [blue]443[/blue] and HTTP on port [blue]80[/blue], transferring the communication to your app."
),
] = 8000,
reload: Annotated[
bool,
typer.Option(
help="Enable auto-reload of the server when (code) files change. This is [bold]resource intensive[/bold], use it only during development."
),
] = True,
root_path: Annotated[
str,
typer.Option(
help="The root path is used to tell your app that it is being served to the outside world with some [bold]path prefix[/bold] set up in some termination proxy or similar."
),
] = "",
app: Annotated[
Union[str, None],
typer.Option(
help="The name of the variable that contains the [bold]FastAPI[/bold] app in the imported module or package. If not provided, it is detected automatically."
),
] = None,
proxy_headers: Annotated[
bool,
typer.Option(
help="Enable/Disable X-Forwarded-Proto, X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Port to populate remote address info."
),
] = True,
) -> Any:
"""
Run a [bold]FastAPI[/bold] app in [yellow]development[/yellow] mode. 🧪
This is equivalent to [bold]fastapi run[/bold] but with [bold]reload[/bold] enabled and listening on the [blue]127.0.0.1[/blue] address.
It automatically detects the Python module or package that needs to be imported based on the file or directory path passed.
If no path is passed, it tries with:
- [blue]main.py[/blue]
- [blue]app.py[/blue]
- [blue]api.py[/blue]
- [blue]app/main.py[/blue]
- [blue]app/app.py[/blue]
- [blue]app/api.py[/blue]
It also detects the directory that needs to be added to the [bold]PYTHONPATH[/bold] to make the app importable and adds it.
It detects the [bold]FastAPI[/bold] app object to use. By default it looks in the module or package for an object named:
- [blue]app[/blue]
- [blue]api[/blue]
Otherwise, it uses the first [bold]FastAPI[/bold] app found in the imported module or package.
"""
_run(
path=path,
host=host,
port=port,
reload=reload,
root_path=root_path,
app=app,
command="dev",
proxy_headers=proxy_headers,
)- CLI 소스코드를 직접 살펴보니 path와 host, port, reload는 기본값이 정해져 있으며 직접 설정도 가능한 것으로 보인다.

- 자세한 사용방법은 fastapi dev --help를 사용하여 확인 가능하다.
def _run(
path: Union[Path, None] = None,
*,
host: str = "127.0.0.1",
port: int = 8000,
reload: bool = True,
workers: Union[int, None] = None,
root_path: str = "",
command: str,
app: Union[str, None] = None,
proxy_headers: bool = False,
) -> None:
try:
use_uvicorn_app = get_import_string(path=path, app_name=app)
except FastAPICLIException as e:
logger.error(str(e))
raise typer.Exit(code=1) from None
serving_str = f"[dim]Serving at:[/dim] [link]http://{host}:{port}[/link]\n\n[dim]API docs:[/dim] [link]http://{host}:{port}/docs[/link]"
if command == "dev":
panel = Panel(
f"{serving_str}\n\n[dim]Running in development mode, for production use:[/dim] \n\n[b]fastapi run[/b]",
title="FastAPI CLI - Development mode",
expand=False,
padding=(1, 2),
style="black on yellow",
)
else:
panel = Panel(
f"{serving_str}\n\n[dim]Running in production mode, for development use:[/dim] \n\n[b]fastapi dev[/b]",
title="FastAPI CLI - Production mode",
expand=False,
padding=(1, 2),
style="green",
)
print(Padding(panel, 1))
if not uvicorn:
raise FastAPICLIException(
"Could not import Uvicorn, try running 'pip install uvicorn'"
) from None
uvicorn.run(
app=use_uvicorn_app,
host=host,
port=port,
reload=reload,
workers=workers,
root_path=root_path,
proxy_headers=proxy_headers,
)- dev, run 함수에서 모두 사용하고 있는 메인 함수인 _run을 살펴보면 매개변수로 입력받은 값들을 설정하거나 기본값을 지정해 uvicorn을 활용하여 run 해주는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
또한, 소스 내부에서 rich 라이브러리 활용하여 비교적 예쁜(?) CLI를 출력해 주는 걸 볼 수 있다.
(rich 라이브러리는 python에서 CLI를 쉽고 빠르고 이쁘게 만들어주는 유용한 라이브러리이다.)
- _run 함수에서는 use_uvicorn_app이란 변수를 app명칭 기본값으로 정해주고 있다. 해당 변수는 get_import_string 함수에서 값을 받아온다.
def get_import_string(
*, path: Union[Path, None] = None, app_name: Union[str, None] = None
) -> str:
if not path:
path = get_default_path()
...- get_import_string 함수를 확인해 보니 get_default_path()라는 함수에서 기본 path를 가져오고 있다. 따라가 보자.
def get_default_path() -> Path:
potential_paths = (
"main.py",
"app.py",
"api.py",
"app/main.py",
"app/app.py",
"app/api.py",
)
for full_path in potential_paths:
path = Path(full_path)
if path.is_file():
return path
raise FastAPICLIException(
"Could not find a default file to run, please provide an explicit path"
)- get_default_path 함수에서는 기본 경로에 해당하는 파일이 있는지 체크를 한다.
기본 파일명은 main.py, app.py, api.py이다.
위 세 가지 명칭은 FastAPI에서 기본 파일명으로 판단하여 자동으로 서버를 띄워주는 듯하다.
마무리
- Fast API CLI 업데이트로 인해 앞으로 Fast API로 신규개발을 할 때, 기존보다 좀 더 빠르고 편하게 개발할 수 있을 것으로 예상된다. 이게 익숙해진다면 기존방식 (uvicorn main:app...) 은 추억 속으로 사라지게 되겠지 그리고 fast api 가 uvicorn 기반으로 서버가 띄워진다는 것도 추후에는 모르는 사람이 생길 수도 있겠단 생각이 든다...(명령어 하나로 손쉽게 서버가 띄워지니까...) 편리한 기능을 만들어준 개발자의 노고를 잊지 말자
'Framework > FastAPI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Fast API] Endpoint Validation (422 Error: Unprocessable Entity) (0) | 2023.09.12 |
|---|---|
| [Fast API] 동기, 비동기 함수 blocking / non-blocking (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| [FastAPI] ASGI uvicorn Server 비동기 동작원리 (0) | 2023.08.26 |

